Introduction
As municipalities, enterprises, and industrial facilities grow more dependent on connectivity, the limitations of traditional hotspot-based WiFi services are becoming painfully clear. High deployment costs, unreliable coverage, and scalability issues make hotspot-based models unsuitable for modern demands.
Enter the multi-hop wireless mesh network — a smarter, more resilient, and future-proof solution. With features like self-healing, self-tuning, and intelligent WiFi mesh networking, these systems deliver superior performance compared to legacy setups.
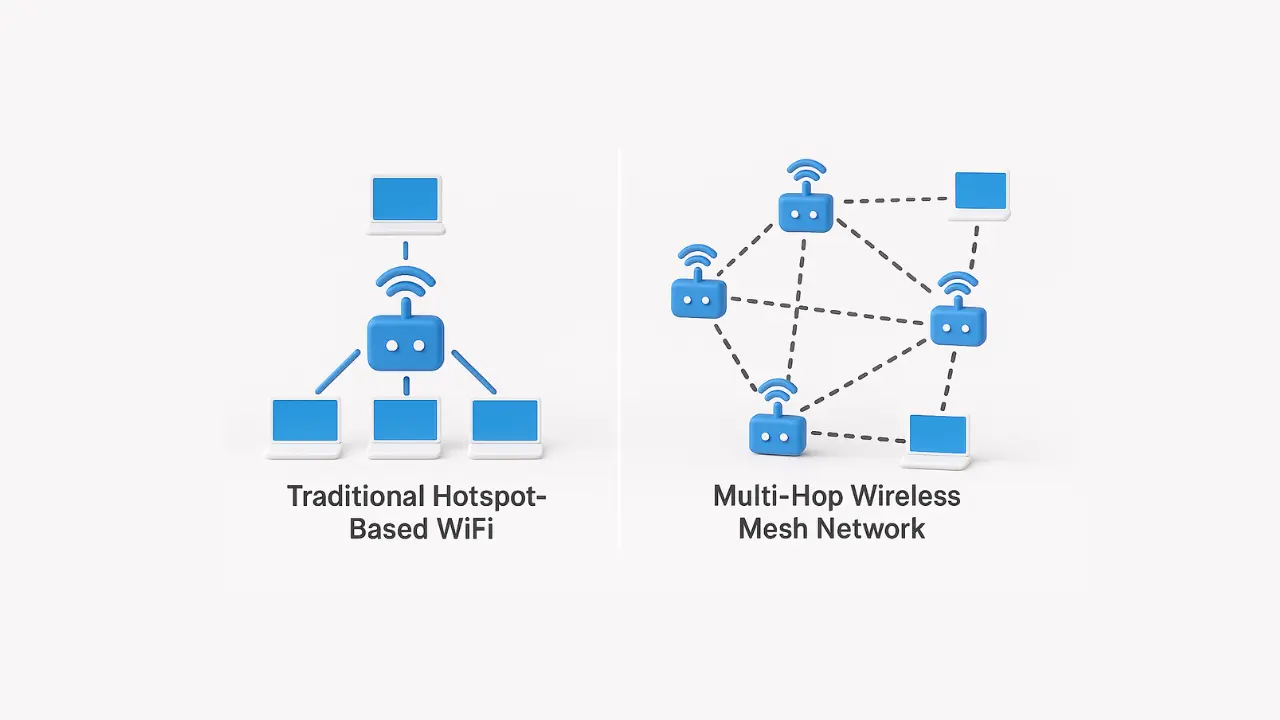
What Is a Traditional Hotspot-Based WiFi Network?
A hotspot-based WiFi service typically connects each access point directly to the fiber backbone. This means that every new installation requires:
- Running fiber to the new site
- Securing approvals and permits
- Dealing with high labor and infrastructure costs
For municipalities or large enterprises, this process is slow, expensive, and difficult to scale.
Why Traditional WiFi Hotspots Fall Short
Despite being widely used, hotspot networks have major drawbacks:
- Limited scalability – Adding coverage requires more fiber
- High deployment costs – Civil works, permits, and manpower add delays
- Vulnerability to outages – Fiber cuts or node failures disrupt services
- High operational overheads – Manual intervention is often needed to fix issues
Simply put: a normal WiFi router or hotspot model isn’t enough to deliver high-performance enterprise-grade connectivity.
What Is a Multi-Hop Wireless Mesh Network?
A wireless mesh network is a decentralized architecture where each access point connects not only to users, but also to neighboring nodes. Instead of relying on a single fiber-fed hotspot, multi-hop mesh networks allow data to travel through multiple access points before reaching the internet or cloud.
Key elements include:
-
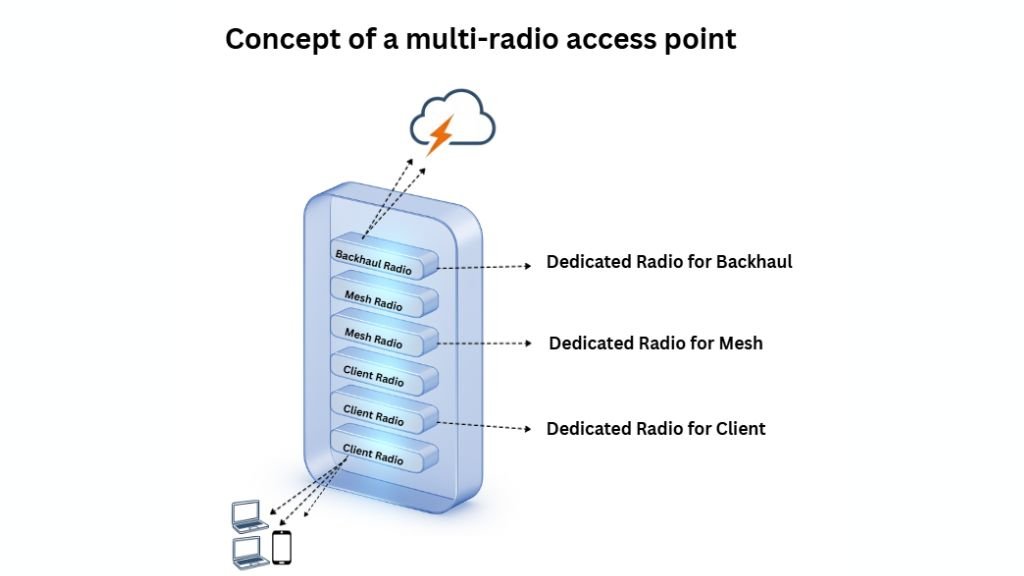
- Multi-radio access points – Some radios dedicated for backhaul (mesh links), others for subscriber access
- Distributed intelligence – Each node scans its surroundings and chooses the best available route
- Cloud-based controllers – Automate configuration and ensure easy onboarding of new nodes
Advantages of Multi-Hop Wireless Mesh Over Hotspot-Based Networks
1. Self-Healing for Continuous Connectivity:
If one node fails due to power loss or interference, the mesh automatically reroutes data through alternate paths. This self-healing ability keeps the network running without manual intervention.
2. Self-Tuning for Peak Performance:
Mesh nodes constantly monitor surroundings and self-tune connections for best throughput and lowest latency. Subscribers always get the most optimal service without service provider intervention.
3. Faster & Cheaper Deployments:
No need to lay fiber for every node. With WiFi mesh networking, providers can rapidly expand coverage in municipalities, campuses, and industrial sites by simply powering up new access points.
4. Scalability Across 10+ Hops:
With dedicated backhaul radios, multi-hop wireless mesh networks can maintain high performance across 10 or more hops, something impossible with traditional hotspot setups.
5. Lower Operational Costs:
Since the network is self-healing and self-tuning, providers don’t need to dispatch teams for every outage or performance issue. This reduces OPEX significantly.
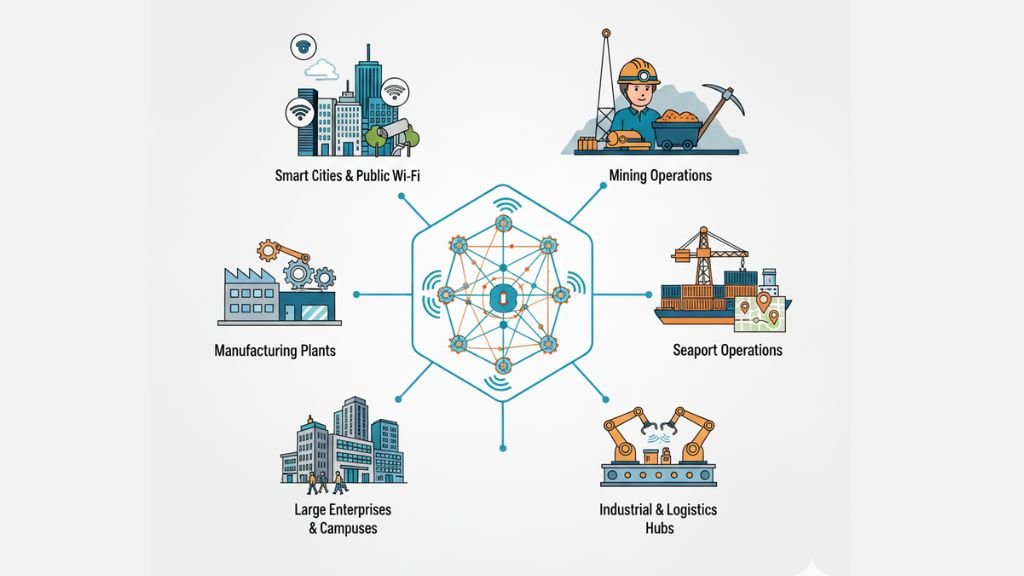
Real-World Applications of Multi-Hop Mesh Networks
-
-
- Municipalities & Smart Cities – Public WiFi, CCTV, and IoT sensors
- Mining Operations – Reliable connectivity across large, remote sites
- Manufacturing Plants – Always-on WiFi for automation, industry 4.0 & robotics
- Seaports & Logistics Hubs – Real-time tracking of cargo and vehicles
- Large Enterprises & Campuses – Seamless WiFi without dead zones
-
Conclusion
For municipalities, mining operations, seaports, and enterprises, the choice is clear: multi-hop wireless mesh networks deliver a level of scalability, resiliency, and cost efficiency that traditional hotspot-based WiFi services simply cannot match.
If you’re looking for the best mesh WiFi solution — one that is intelligent, self-healing, and future-ready — multi-hop wireless mesh networking is the answer.